고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
Now you can upload your notes at EazyNotes. Just click and submit your notes. After reviewing, they will be published under your name.
So, what are you waiting for. Submit your notes and share them with the world.Subjects. INTRODUCTION TO IT.
MS-OFFICE. PROGRAMMING IN C. C. JAVA. DATA STRUCTURES. COMPUTER GRAPHICS.
COMPUTER NETWORKS. OPERATING SYSTEM.
8086 Microprocessor Notes Pdf
DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM. DIGITAL CIRCUITS & LOGIC DESIGNS. MICROPROCESSOR. COMPUTER SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE.
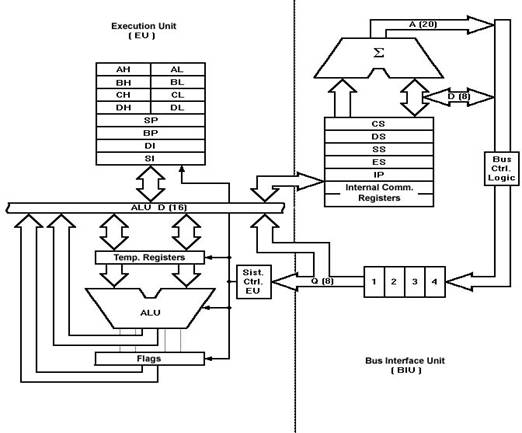
Block Diagram 8086 Microprocessor Pdf Format
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM. WEB DEVELOPMENT. To tell BIU where to fetch the instructions or data from. To decode the instructions.
To execute the instructions.The EU contains the control circuitry to perform various internal operations. A decoder in EU decodes the instruction fetched memory to generate different internal or external control signals required to perform the operation. EU has 16-bit ALU, which can perform arithmetic and logical operations on 8-bit as well as 16-bit.General Purpose Registers of 8086These registers can be used as 8-bit registers individually or can be used as 16-bit in pair to have AX, BX, CX, and DX.
AX Register: AX register is also known as accumulator register that stores operands for arithmetic operation like divided, rotate. BX Register: This register is mainly used as a base register. It holds the starting base location of a memory region within a data segment. CX Register: It is defined as a counter. It is primarily used in loop instruction to store loop counter. DX Register: DX register is used to contain I/O port address for I/O instruction.Segment RegistersAdditional registers called segment registers generate memory address when combined with other in the microprocessor.
In 8086 microprocessor, memory is divided into 4 segments as follow:Fig. 2: Memory Segments of 8086. Code Segment (CS): The CS register is used for addressing a memory location in the Code Segment of the memory, where the executable program is stored. Data Segment (DS): The DS contains most data used by program. Data are accessed in the Data Segment by an offset address or the content of other register that holds the offset address.
Stack Segment (SS): SS defined the area of memory used for the stack. Extra Segment (ES): ES is additional data segment that is used by some of the string to hold the destination data.Flag Registers of 8086Flag register in EU is of 16-bit and is shown in fig. 3: Flag Register of 8086Flags Register determines the current state of the processor. They are modified automatically by CPU after mathematical operations, this allows to determine the type of the result, and to determine conditions to transfer control to other parts of the program. 8086 has 9 flags and they are divided into two categories. Carry Flag (CF): This flag indicates an overflow condition for unsigned integer arithmetic.
It is also used in multiple-precision arithmetic. Auxiliary Flag (AF): If an operation performed in ALU generates a carry/barrow from lower nibble (i.e.
D0 – D3) to upper nibble (i.e. D4 – D7), the AF flag is set i.e. Carry given by D3 bit to D4 is AF flag. This is not a general-purpose flag, it is used internally by the processor to perform Binary to BCD conversion.
Parity Flag (PF): This flag is used to indicate the parity of result. If lower order 8-bits of the result contains even number of 1’s, the Parity Flag is set and for odd number of 1’s, the Parity Flag is reset. Zero Flag (ZF): It is set; if the result of arithmetic or logical operation is zero else it is reset. Sign Flag (SF): In sign magnitude format the sign of number is indicated by MSB bit. If the result of operation is negative, sign flag is set. Overflow Flag (OF): It occurs when signed numbers are added or subtracted. An OF indicates that the result has exceeded the capacity of machine.Control FlagsControl flags are set or reset deliberately to control the operations of the execution unit.
Control flags are as follows.




